Hydration and Supplements.

Good morning people of the internet, today I bring you an article all about body composition changes. This time focusing on hydration and supplements. If you missed the last 2 articles, I went over the other key pillars you should stick to, to see body composition progress. They were food composition and nutrient timing and a brief bit of information about macronutrients and micronutrients. Here is the link to that article: https://www.theavgguysnutritionandexerciseguide.org/nutrition/dieting-for-body-composition-changes/. Before that particular article I explained a little about calorie balance and macronutrient amounts. Here is the link to that article:https://www.theavgguysnutritionandexerciseguide.org/nutrition/total-nutrition-part1/. Please read each of them in order. In this article, if you apply the information you are going to read you can expect to see a 5% difference in your body composition results. So without further a do, let’s jump into today’s article and learn all about hydration and supplements.
Hydration.
Hydration is relatively straightforward when it pertains to health, performance and body composition changes. Being sufficiently hydrated for the normal healthy functioning of the body is the same when you are well hydrated for high performance. Drink when thirsty and when your body is calling out for some fluids. Performance is only affected by a small degree when you are under or over hydrated. So my advice is to allow your body guide you and you shouldn’t go too far wrong.
A supplement is a supplement to an already solid diet.
Then we have supplements. A lot of people for some reason or another like to put a huge emphasis on the potential of supplements to dramatically make body composition changes and increase strength and power. This is probably down to the marketing of big supplement companies. But if you think about it. Do you think consuming creatine powder everyday or making sure to consume enough protein to repair and build more muscle tissue both rank equal on the ladder of importance? Definitely not. Consuming enough protein daily will always rank ahead of consuming creatine everyday since protein and amino acids are the very building blocks of muscle tissue. Creatine is not. It is just a supplement to a diet already high in protein.
Let your common sense guide you.
Another example could be pre-workout powders. Yes they may give you some energy, reduce levels of tiredness if you are feeling so before or during a workout. Some ingredients can help you acquire a better “pump” while exercising your muscles. But if you start to rely on pre-workout everyday eventually your going to hit a point when your body is not going to respond to it as well as it has been doing. Why? Because the body adapts. What worked in the past does not work anymore or not as well as it once did. What is way more important to make meaningful body composition changes is consuming adequate amounts of carbohydrates leading up to training and afterwards. To fuel performance in the gym and and increase the anabolic effects of increased insulin levels after training as blood insulin levels are temporarily for the next 3- 6 hours. Supplements do not help here either.
Hydration.

Hydration is the degree to which different parts of your body are hydrated or contain enough water. Its important to be well hydrated as hydration is linked to performance. Better performance in the gym means improved better composition changes. At any one time your body can be in 1 of 3 states of hydration: Dehydration, euhydration and hyperhydration. The first meaning your body does not contain enough water to function as best as it can. The 2nd meaning you have enough water within your body to perform/carry out tasks well. Lastly we have hyperhydration which means you have too much water present in your body which also negatively affects you just like being dehydrated does. To be honest only if you are excising in very humid conditions or you carry out a water cut, can you notice a drop in performance.
How to prevent dehydration.
When you are exercising in humid conditions, you’ve after completed a tough training session or match, or your sweating a lot. By the time you feel thirsty, you are a little dehydrated.
Track your urine color.
When your hydrated your urine color should look like lemonade or slightly yellow. Make sure to track your urine color over days instead of hours as consuming a lot of fluids quickly or alcohol can hide your true state of hydration. If your urine color is a dark yellow, you are dehydrated and should consume enough fluids to reach hydration. Likewise if your urine color is clear your probably drinking too many fluids. You can also observe this when you consume caffeine, which is a natural diuretic. So the color of your urine is clear as the water you recently consumed is flushed out again by your body.
Track your bodyweight.
Daily fluctuations in weight are usually due to fluid changes. If you train intensely or compete in a competitive sporting event, make sure to weigh yourself afterwards to measure water loss and re-hydrate sufficiently.
Consume 1.5ml of water per kcal eaten.
This one is only needed if you want to be optimally hydrated for sports competitions or high performance events. If you are dieting (purposely under eating calories) or your sweating a lot you may need more. Under isocaloric conditions or eating enough calories to maintain your bodyweight, 1.5ml per kcal eaten is plenty.
Degree of hydration and dehydration.
We know once you are sufficiently hydrated or even a little dehydrated one of these levels of hydration will be enough to support your performance in training, on the pitch or court. But the more dehydrated you are, the greater the health risks and a larger decrease in performance is observed. Make sure to track your hydration levels by measuring body weight daily.
Mild dehydration.
Mild hydration is the first level of dehydration. When you experience mild dehydration you feel thirsty. You can’t focus. Maybe you experience mild fatigue. You may also notice small decreases in strength and athletic performance. If you wish to compete at a high level, as you have just read you can’t afford to be mildly dehydrated. If the other athlete or team are sufficiently hydrated, they have a performance advantage over you. This could be enough to tip the balance in their favor.
Moderate dehydration.
When you are at this stage of dehydration, you have a harder time focusing. Greater decreases in strength and athletic performance are noticed, there is a greater risk of overheating and you sweat less. With the last making it easier to overheat since sweating helps the body stay at hydration homeostatis. Your urine color will be yellow and can be a way to check if you are at this stage of dehydration.
Severe dehydration.
When you are severely dehydrated, you may observe increased muscle cramping. A higher respiratory rate or breathing quicker than normal. Decreased cardiac output. Chills up and down your body. A rapid pulse and symptoms of heat exhaustion like weakness, nausea and dizziness.
Extreme dehydration.
When you are extremely dehydrated you will notice being dizzy, muscle spasms, poor balance when standing, walking or moving. Possibly fainting, hallucinations, possible heat stroke and a very high body temperature. Possible loss of consciousness, shock and coma and maybe even death. Of course we hope to never experience this but it’s good to know these side effects just in case.
I’d like to finish this part by mentioning you have probably heard of athletes doing weight cuts by consuming less water or sweating out the fluid in their body. Unless you are an experienced athlete who has accepted the possible negative consequences and is happy with them to achieve the desired result, I wouldn’t try weight cutting by manipulating water just to “try it”. Don’t cut down more than 10% of your bodyweight while using a water cutting technique if your happy with your decision to go ahead with it.
Hydration protocols.

Pre-session.
While training we can experience slight dehydration and a fluid loss of 2x of our body weight compared to what our gastrointestinal tract can absorb per hour. Before training or pre compitition make sure to measure bodyweight and urine color. If on a massing phase or dieting to build muscle or lose body fat respectively, tracking your urine color is the best way to gauge your level of hydration.
Intra-session.
While training you should be consuming 5 fluid ounces per 20 minutes of hard training to reach hydration. This can be lower in cooler environments or when carrying out less intense exercise or higher when exercising more intensely and in more humid environments. Make sure you are consuming electrolytes through powders, tablets or a sports drink.
Post session.
A third of the water you consume is lost in urine leaving the body. The GI tract does not absorb all water consumed. A general guideline could be to consume 8oz of fluid every 15 minutes until you reach hydration. Also if your lose for example 2ibs of water through sweat you need to drink 3ibs of water post training to reach hydration. Makes sure to consume water with food and electrolytes as you will reach hydration faster.
Hyponatremia.
Hyponatremia is a condition which occurs when you consume a large quantity of water but without enough electrolytes. Leading to a low electrolyte balance. This could be like when drinking a lot of water (3-4L) all in one go after physical exercise. You see as you urinate throughout the day you lose electrolytes. Just consuming more water is not going to replace these lost electrolytes. If you do not consume enough or replace lost electrolytes, this leads to reduced functioning of the nervous system, the skeletal muscles, the heart and eventually death. While on a hypocaloric diet, you are also at risk as you are taking in less foods and fluids in general. If you don’t consume a lot of salt you are also in the danger zone. The warning signs to look out for are muscles spasming, muscle weakness, cramping, low energy, mental fatigue and headaches.
Preventing hyponatremia.
To prevent any of these side effects happening to you, make sure to consume a drink with a high electrolyte content during and after exercise. If you are only consuming water, only drink a liter at a time, drink slowly and consume with food.
Supplements

Finally we have come to supplements. Probably there are some people out there who couldn’t wait to get to this part to read all about the wonder supplement that will help them build muscle or strength way faster than which you normally could with just a solid diet or lose fat easier. A lot of people overestimate the power that supplements actually have to make body composition changes. Well to cut to the grain, no supplement is so strong that it will cause dramatic effects such as those mentioned. Unless you are talking about PED’s or performance enhancing drugs which can for sure help with those aforementioned points. But they also carry health risks and they are not regulated since its illegal to consume them. It’s probably a wise decision to stay away from all types of PED’s and stick to the tried and tested supplements. When it comes to some supplements, sometimes you may not be able to even trust what the label or salesperson tells you, so be wary when choosing yours.
Beware when choosing your own supplements.
When I talk about supplements I mean supplements that will help you build muscle, strength and and lose fat quicker and more effectively than what a normal diet could do. But a lot of the supplements out there, don’t even work given their chemical structure. When choosing to buy a supplement, make sure to look at supplements where a large body of research has been carried out. Review articles written by dieticians, people who are experts in this field can be trusted. Look for supplements where multiple review articles have been written about them and they find the same or similar findings. Long-term studies are useful as the longer a supplement is studied the more thorough the research. Independent labs can also be trusted.
Nothing beats trying it for yourself.
Did you know supplement companies can pay labs to help them make a supplement seem more appealing? Actually using the supplements yourself and seeing the results first hand is also a useful approach. Maybe 1 supplement works well for your friend but not for you? When making a final decision on using a supplement for improved body composition changes look at real world feedback, make sure there is enough data history and there has been an agreement on certain benefits amongst reviewers.
Supplements which have been proven to work.
Yes some don’t work, but there are a few that have been consistently shown to work for different people. These include:
- Caffeine.
- Whey protein.
- Casein protein.
- Creatine.
- Carbohydrate drinks.
- Multivitamin supplements.
- Omega 3 fish oil supplements.
1. Caffeine.
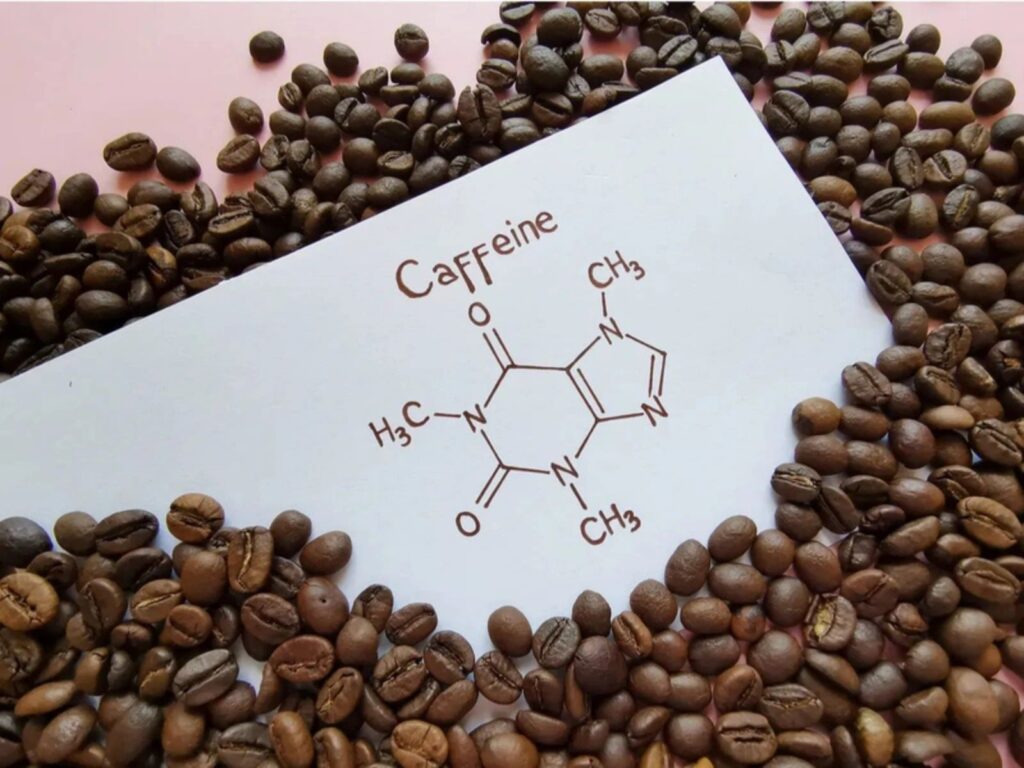
Firstly, we have caffeine, which is a sympthomimetic and belongs to a family which exhibit the same effects when taken. It has been thoroughly tested down through the years and it’s effects have been well documented. It helps to activate the fight or flight response. In the past this helped us to run away from dangerous animals or humans. Or maybe fight them if you felt the odds were in your favor. Now we don’t really need this response for those purpose’s but these very responses helps to enhance our sports or gym performance as well as inhibiting feelings of hunger. Of course this is of interest to those of us, who wish to improve performance and body composition. The full list of benefits includes:
- Greater alertness.
- Greater tolerance to pain.
- Improved repetition performance and endurance.
- Increased levels of motivation.
- Decreased hunger.
Caffeine can be a powerful tool for some.
All of these benefits can really come in handy while training or during different phases of training. In my own training I have used caffeine to enhance my performance when I was feeling particularly tired with a lot of work during the week. A perfect example could be when you know you have heavy squats and deadlifts coming up later. You know it’s going to hurt. It won’t be easy. But caffeine will help you tolerate the pain which comes with training legs to a greater degree and you have more motivation to go in and get it done. Caffeine can quiet literally change your state before going into a session and the results that follow. It can help to keep you going in the right direction with your own body composition changes. Another great time to use it is while dieting. You are consuming less food than you normally would, your energy levels are lower, the sessions are that little bit harder. Caffeine used smartly will help you get through the toughest sessions and keep you headed in the right direction. So instead of experiencing poor sessions while dieting which could lead to negative body composition changes such as muscle loss. (If you are not training hard or frequently enough) You can have better sessions which allow you to hold onto the positive body composition changes you have been making the last few weeks and months.
A sneaky hunger suppressant.
Another side benefit is caffeine helps to suppress hunger which is useful while dieting. I know for one, I am someone who loves food and seem to think about it a lot while going about my day. Caffeine helps me to “switch off” and focus on other tasks, ultimately helping me to hit a caloric deficit and lose my target weight for that day or week. For those quiet sensitive to caffeine, make sure to limit or stop intake after noon since you may notice you have problems sleeping well. In the ladder of importance sleep will always come before how much caffeine you take.
2. Whey protein.
Next we have whey protein. Ah I remember the days when the guys at school would be buying whey protein to help them “get huge” for the upcoming rugby season. Yes it will help but it’s not like it’s magic! So whey protein, is one of the highest quality protein sources, scoring over 100 on the protein quality index scale. It is fast digesting which makes it suitable to be taken as part of an intra-workout shake or straight after your workout when blood insulin levels are elevated. This type of protein is derived from milk products. There are actually 3 types of whey protein. Concentrate, which is the least pure. Isolate which is intermediately pure and hydrolysate being the purest of all. The more pure the protein is, the more costly and that might make the concentrate version the best bang for your buck when taking, cost and quality into consideration. If you experience gastrointestinal distress, isolate may be better. If sensitive to dairy, hydrolysate could be a better option.
3. Casein protein.
Casein protein, also derived from milk products like whey protein is another high quality supplement. Though unlike whey protein, casein takes 7 hours to be fully digested and absorbed by the body. This uniqueness makes it a great option to take before bedtime as your not going to be consuming any type of protein while you sleep. Or when not eating for a long period of time, like while busy at work or you have a busy schedule all day. I would personally use it before bedtime and pair it with a fat source to help slow down digestion even more. For a gradual release of amino acids throughout the night.
Creatine.
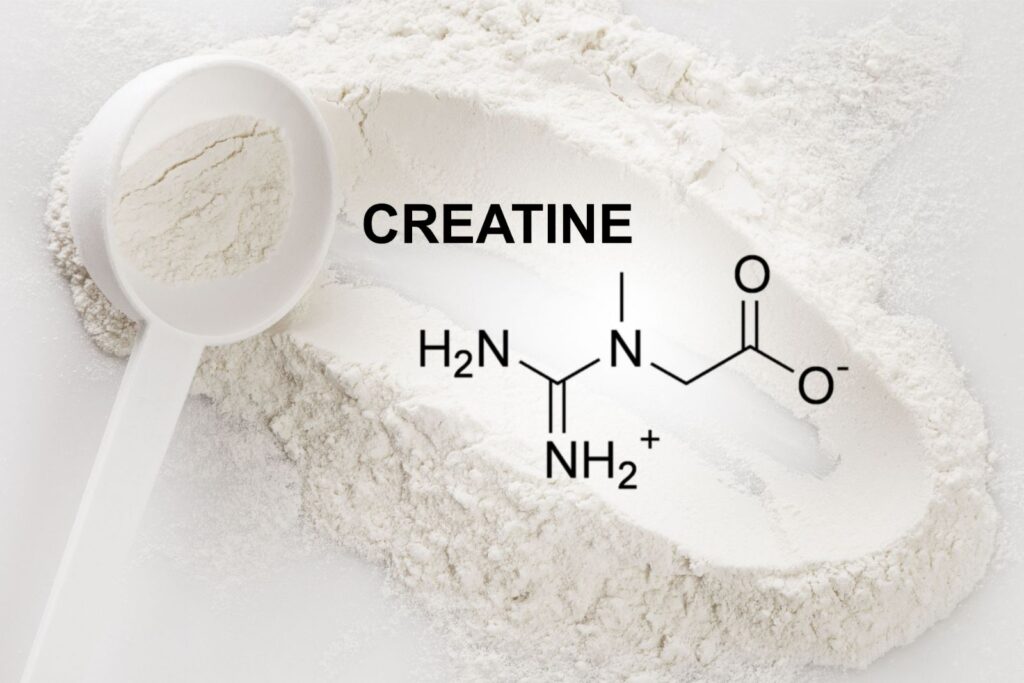
Creatine occurs naturally in our bodies. In muscle tissue it acts as a buffer to ATP or Adenosine Triphosphate. ATP is a molecule which stores energy from food and fuels a lot of cellular reactions one of them being muscular contraction. As humans, we have a limited supply and only have just enough to fuel all out max muscle exertion for 1-3 seconds. After 3 seconds, ATP stores need to be refilled. The creatine phosphate system is the best way to do this. Creatine is very helpful when looking to increase near max muscle exertions. Where usually you may be able to perform 10 repetitions with 2kg on tricep dips, after taking creatine at least for a couple of days you should see an increase in repetitions performed. Maybe you can perform another 3-4 repetitions with the same weight compared to under training conditions without supplementing with creatine.
Just a little bit of science.
A little bit of science here. Hard training depletes phosphates. Phosphocreatine gives phosphates to depleted ADP, turning them back to adenosine triphosphate. A phosphate which lacks creatine, can receive more phosphates to give to ADP and so repeats the process.
Creatine has been shown to lead to more muscle retention as well as greater muscle growth and strength. Increased muscle retention and growth is due to extra cell swelling which has been shown as an independent driver of muscle growth. Or because of being able to tolerate higher volumes and being able to train at a higher intensity both helping you to increase muscle mass. As creatine helps with the phosphate system, people with a greater proportion of fast twitch fibers benefit more from supplementing with creatine. Vegans and vegetarians can also benefit due to not consuming animal proteins such as red meat which contain a lot of naturally occurring creatine. While supplementing with creatine your body weight can increase by as much as 3% due to intramuscular swelling which gives you the appearance of having larger and fuller muscles. When looking to choose a type of creatine to supplement with, choose creatine monohydrate which has been tested extensively, being proven to enhance performance and muscle size.
Multivitamins.

Multivitamins are important as they contain micronutrients which allow our bodies to absorb food better, sleep better, have increased levels of energy and better absorb food among other things. If you consume enough fruit and vegetables, wholegrains, lean proteins and healthy fats you will hit your micronutrient requirements. If your dieting, it may be wise to take a multivitamin supplement which acts as an insurance policy against micronutrient deficiencies. Your at a greater risk of lacking in some micronutrients while dieting as your consuming less total calories. That’s why it’s really important to consume only healthy foods while dieting to hit all of your micronutrient requirements.
It must also be mentioned that some processed foods such as white rice and pasta lack micronutrients. Since during processing, these foods have been stripped of their fiber and micronutrients. While dieting I would not consume processed foods and carbohydrates for the reason they lack micronutrients and fiber. While looking to gain weight, they can be very useful. So to finish with multivitamins, if your eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables and wholegrains you probably don’t need to take a multivitamin supplement. While dieting it could be a good idea.
Omega 3 fat supplements.
Omega 3’s can be found in fish and also in Omega 3 supplements. These essential fatty acids help to improve cognitive function. It was thought they may also help with improved cardiovascular function but this has been put into doubt. Make sure to consume the minimum amount of these essential fatty acids for the normal functioning of your brain. This would be 0.3g per ib of bodyweight. I would recommend to consume an omega 3 supplement if your diet lacks in fish and seafood. Maybe you don’t eat a lot of fish because it’s expensive or you don’t really like the taste. Whatever your reason, an omega 3 supplement may just be the trick for you.

So there you have it, a little bit more knowledge on hydration and supplementation. I hope you use this information wisely to reach your own body composition goals. I would love to hear what you thought of the article and if your willing please comment down below what information you found useful. Please stay tuned, as I will be realizing a new article very soon. Have a great rest of your training week!
